HOW TO PROTECT ELECTRONIC DEVICES FROM ESD DAMAGE DURING SHIPMENT
Posted: October 23th, 2019 Author: Jim Higgs
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What Are the Different Types of ESD Packaging?
Standards and Regulations for ESD Packaging
Deciding on the Best ESD Packaging for Your Application
How to Properly Pack Components to Prevent ESD
When you package a product for shipment, there are always a few worries that cross your mind. What if the package is dropped? What if the storage container floods? Will the packing materials be able to withstand vibration? The last thing any manufacturer or supplier wants is to see their product come out from the shipping process visibly damaged. However, electronics manufacturers and suppliers have an additional invisible threat to consider that could render their products unuseable — ESD.
WHAT IS ESD?
ESD is short for electrostatic discharge. This discharge occurs when the surface of an object builds up an abundance of electrons, creating a voltage potential. As soon as that object touches another object with a lower voltage potential, the charge jumps between them, creating a small electric shock or arc.
A common example of ESD occurs when you rub your feet on a carpet and go to touch something metal or shake someone else’s hand. That small electric shock is ESD. While ESD may seem harmless on the surface, it can be devastating for computers and electronic components. Each year, vast numbers of electronic devices are destroyed or damaged by electrostatic discharge.
WHY DOES ESD OCCUR?
ESD can occur in many environments relating to the electronics industry through two different processes. These are explained in detail below:
- Tribocharging: This occurs when two materials repeatedly touch and separate or rub together. This results in a gradual buildup of voltage potential. Tribocharging is how one builds up an electric charge when walking across a carpet.
- Electrostatic induction: This occurs when an electrically charged item is placed near a conductive object. If the conductive object is insulated, or removed from the ground, it will build up a charge just by being close to the electrically charged item. As soon as the charged conductive object touches another conductive object, it will result in an ESD.
Both causes of ESD buildup can affect electronics at every stage. Poor grounding in an electronics repair shop can result in tribocharging that can damage computers and components. Proximity to electrically charged items and conductive objects may result in damage to equipment in manufacturing plants. ESD through electrostatic induction can even occur within a device — antennas can act as paths for ESD to enter the system, while unnecessarily high-speed devices can radiate ESD.
Shipping is a particular area of concern for manufacturers and suppliers. The vibrations involved in many forms of transportation can result in tribocharging that causes parts to build up an electric charge. Most commonly, plastic parts within and around machines may rub against one another and build up an electrostatic charge that has the potential to cause ESD damage.
ESD-SENSITIVE COMPONENTS
ESD can have adverse effects on electronic devices at any level of completion. From board manufacturing and testing to component and product assembly, ESD poses a significant threat. Electrostatic voltages as low as 30 volts and currents as low as 0.001 amps, which is lower than what the human body can sense, can damage electronics. Modern electronic components are at a heightened risk of ESD two major reasons:
- Devices today have progressively smaller and more sensitive parts and thinner protective layers
- Shipping components long distances is increasingly common, putting them at increased risk of damage

Some examples of common ESD-sensitive components include the following:
- MOSFET transistors used to make integrated circuits
- CMOS devices, which tend to have smaller geometries
- High precision resistors
- Laser diodes
To help protect these essential components from ESD-related damage, organizations have worked toward developing ESD protection methods.
HOW TO PREVENT ESD DAMAGE
Preventing ESD-related failures takes planning, but there are many ESD precautions you can take. Some of the ESD protection basics to consider when determining how to protect electronics from EMP and ESD include:
- Design against ESD: ESD prevention begins with circuit design. Proper design helps minimize potential ESD damage through grounding and layout techniques.
- Practice ESD management: Careless handling of electronics is the primary reason for ESD-related failures. To prevent this, individuals handling electronics must practice basic ESD elimination techniques, including wearing a ground-connected wrist strap, using a grounding pad, keeping work areas free of static-generating materials and storing components properly.
- Watch the humidity: Relative environmental humidity above 40 percent reduces the resistance of items that may generate a charge. This makes it more difficult to generate voltage potential, effectively reducing the potential for ESD. Humidity should be kept beneath 80 percent in order to avoid corrosion.
- Use anti-static packaging: ESD packaging is one of the most effective tools for protecting against ESD. Components can be stored in anti-static packaging when not in use, protecting them from ESD from any source. This is also one of the most effective ways to prevent ESD-related damage during shipping.
While basic safety practices show you how to prevent electrostatic discharge from damaging equipment, one of the most important ESD prevention tactics is using ESD packaging.
HOW DOES ESD PACKAGING WORK?
When packaging sensitive electronics for shipment, you may wonder how to eliminate electrostatic discharge and prevent it from damaging your shipment. The best way to accomplish this is with ESD packaging. Normal packing materials won’t protect against electrostatic buildup and discharge during the shipping process, but ESD packaging will.
ESD packaging materials resist the buildup of a charge, preventing charges from entering or exiting the packaging. Instead, the charge flows around the packaging, preventing a spark from occuring. ESD packaging creates what is known as a Faraday cage around the shipped item. But what is a Faraday bag, and how does a Faraday cage protect electronics?
ESD packaging and Faraday bags are made using anti-static materials treated with special chemical coatings. For example, polyethylene bags normally wouldn’t protect against ESD, but they can be treated with anti-static chemicals to create a low-charging protective packaging. The best thing is that ESD packaging materials come in all shapes and sizes, including standard packaging items like poly bags, foam, boxes and even bubble wrap.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF ESD PACKAGING?
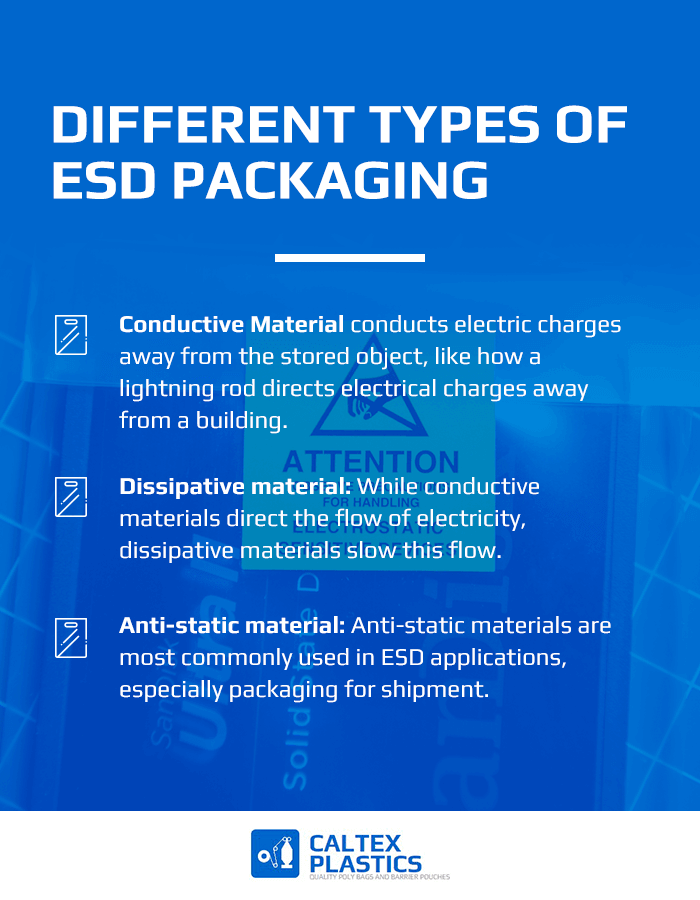
There is a wide variety of ESD packaging options, but they all fall into one of three categories based on the material used:
- Conductive material: Conductive material conducts electric charges away from the stored object, like how a lightning rod directs electrical charges away from a building. This material prevents a charge from building in and around the stored materials.
- Dissipative material: While conductive materials direct the flow of electricity, dissipative materials slow this flow. These materials reduce the strength of the electrical charge, protecting the stored materials from strong charges.
- Anti-static material: Anti-static materials are most commonly used in ESD applications, especially packaging for shipment. Anti-static materials inhibit tribocharging by preventing the buildup of static electricity.
Of these materials, anti-static materials are most commonly used in packaging. However, all three can be used, depending on your needs. All ESD packaging materials can be used in a range of forms to suit your specific applications. Some examples are provided below:
- Stretch film: Stretch film is shrink wrap that is treated with chemicals to instill ESD preventative properties. It tends to be anti-static. You can use it like normal shrink wrap and apply it by hand or by machine to pallets, packages or individual items.
- Bags and tubing: Plastic bags and tubing come in a range of materials depending on the needs of the application. You can use these items for individual wrapping of electronics of varying sizes.
- Shielding bags: Static shielding bags are significantly more effective than typical anti-static bags. These bags work by acting as Faraday cages around individual products, dispersing electromagnetic charges along the exterior surfaces of the pouches. These faraday bags are made of aluminum and treated plastic.
ESD packaging materials may also have additional properties to protect sensitive components from other potentially damaging factors, such as moisture and vibration. For example, Caltex provides materials with unique barrier properties against several sources of contamination and damage, including water vapor, air, static electricity and electromagnetic interference.
STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS FOR ESD PACKAGING
In the United States, the most significant standards and regulations for ESD packaging come from the American National Standards Institute, or ANSI, and the EOS/ESD Association, also known as the ESDA.
ANSI is an organization of professionals that specialize in writing standards for a wide range of industries, including the electronics industry. The ESDA, on the other hand, is an association of electronics and electronic packaging industry professionals that focus on and provide guidance for ESD avoidance. ANSI and the ESDA provide the following:
- Design standards
- Standard test methods
- Standard practices
- Technical reports
- Informational advisory documents.
These ESDA standards and specifications alone are used by almost 16,000 members across more than 55 countries.
Why use ANSI and ESDA standards? The biggest reason is that ANSI and ESDA standards are industry standards. All professionals in the industry understand ANSI and ESDA certification as a sign that an ESD control product or method works. ANSI and ESDA standards provide objective evaluation measurements and communicate to electronic component manufacturers and handlers that they can trust a given product.
DECIDING ON THE BEST ESD PACKAGING FOR YOUR APPLICATION
There are many things to consider when determining the best ESD packaging for your application. If you’re not sure how to protect your electronics from ESD during shipment, the user guide EN 61340-5-2, a British standard, provides some guidance as to how to select the best packaging solution. The basic guidelines are detailed below:
- Determine product sensitivity: Gather information about the ESD sensitivity of an item. This can be done through in-house measurement or by contacting the manufacturer.
- Determine the shipping environment: Knowing how the product will be handled, as well as the humidity and temperature it will encounter, plays a significant role in determining appropriate packaging. For example, moisture-sensitive components should be stored in ESD packaging with a barrier material to prevent excessive exposure to humidity.
- Determine your company’s needs: Analyze the application in which this packaging will be used and decide whether you need to make any adjustments to accommodate your company’s specific requirements. Is reusable packaging desirable and practical? Is the aesthetic appearance of your packaging important for your brand?

Once you have determined your basic needs, work with your packaging provider to create a solution that fits your needs. Before full implementation, however, be sure to test the final packaging product under normal and extreme conditions to ensure that your products will be protected. For example, your company can do high voltage discharge tests, simulate over-the-road vibration, conduct drop tests or expose the packaging to extreme environmental conditions to see how well it holds up.
You can also refer to standards to help determine the best packaging for your application. For example, the ANSI/ESD S541-2018 delineates the properties of ESD packaging materials, what is necessary to protect against ESD and the packaging requirements needed to achieve ESD protection.
HOW TO PROPERLY PACK COMPONENTS TO PREVENT ESD
If you’re wondering how to properly ship electronics to prevent ESD, there are many factors to consider. However, there are three basic ESD protection methods to keep in mind. These are detailed below:
- Use shielded containers: This may seem like a no-brainer, but it’s something that many neglect to address. Instead of using appropriate shielded containers for highly sensitive devices, they use non-shielded containers with basic static shielding bags. While non-shielded containers provide physical protection and tend to be cheaper, they provide no protection from ESD, and static shielding bags may be insufficient depending on the component in question. Using an appropriately shielded container is far less expensive in the long run than replacing damaged parts
- Use a lid: This is another step that may seem simple but is often forgotten or overlooked. The Faraday cage effect can only work if the contents of the cage are surrounded on all sides.
- Avoid damaged packaging: While replacing shielded containers may be expensive, a damaged container is a risk to your shipment. Holes, tears and gaps leave the contents of a shipment vulnerable to ESD.
If you’re still not sure what you need for your application, work with your packaging provider to determine how to package electronics so that they are protected both from physical damage and from ESD damage. Don’t have a packaging provider that can help you with ESD precautions? Consider partnering with Caltex Plastics.
CHOOSE CALTEX PLASTICS FOR YOUR ESD PACKAGING NEEDS

If you’re looking for an ESD Packaging producer that can tailor packaging to your product’s specific needs, Caltex can help.
At Caltex Plastics, we specialize in protecting electronics from ESD. We produce a variety of ESD packaging solutions, including custom bags, pouches, tubing and sheeting. Since 1984, we’ve provided our customers with affordable packaging solutions tailored to their needs with quick turnaround times and excellent customer service. Our multi-layer barrier solutions use high-quality materials and are laboratory tested to ensure they meet stated specifications.
At Caltex, you are our top priority. We ensure that we are ready to serve our customers by having the largest selection of rollstock in the industry on hand across our extensive warehousing network. By operating 24/7 and maintaining an inventory of quality supplies, we can offer top-notch service and delivery times. With Caltex, you can expect excellent results every time.
If you’re interested in partnering with Caltex for your ESD packaging needs, contact us today to learn more.